A Product Marketing Manager (PMM) bridges product, marketing, and sales, driving adoption through research, positioning, messaging, and launches. Success requires communication, analytics, collaboration, and strategy, with growth opportunities across industries, using tools, trends, and cross-functional teamwork for impact.
It is one of the most dynamic roles in our marketing ecosystem. But what does a Product Marketing Manager (PMM) do, to be exact? And why are they critical to a product’s success?
Whether you’re a business student in the process of mapping out a career, a marketer seeking out new opportunities, or a product manager interested in the overlap between marketing and product development, this guide will help you break it all down. In this article, we will look at what it takes to be a Product Marketing Manager, their duties, skills required, and how you can kick-start this great career.
What is Product Marketing and Why Does It Matter?
Simply put, product marketing is what connects product design and consumer demands. It guarantees that a product is well-researched yet fits the proper market and is effectively positioned for adoption and engagement. Where the product team makes sure a solution works, the product marketing team makes sure that solution matches the audience.
Like their biological counterparts, product marketing managers sit between product, sales, and traditional marketing. Specifically designed, they fit the product precisely in the market and place it right in front of the right customer at the right time. This kind of role is essential in industries with fierce competition or in companies launching new products and features often.
The Core Responsibilities of a Product Marketing Manager
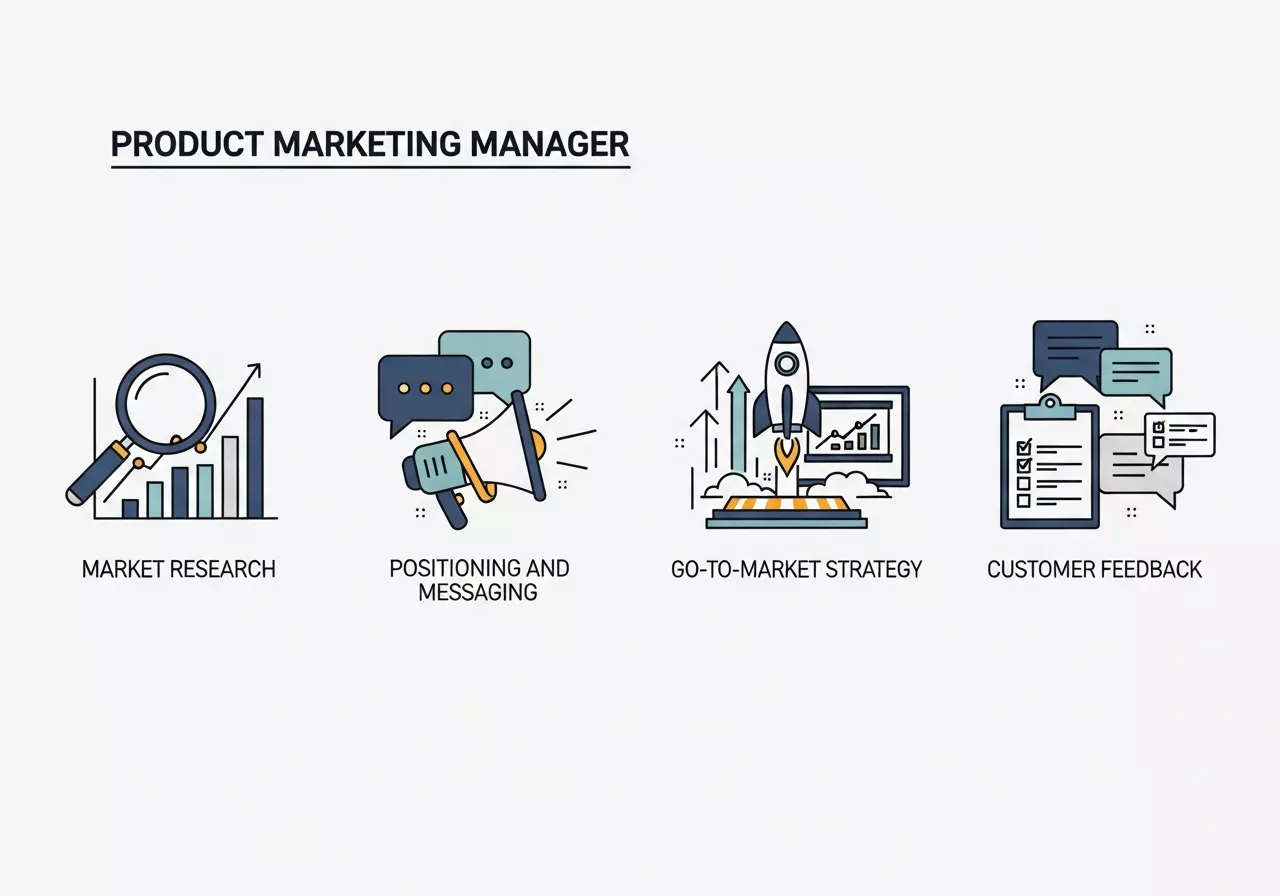
PMMs wear many hats, which makes their role both challenging and rewarding. Here are the key tasks that define their job:
1. Market Research
One of the foundational responsibilities of a PMM is understanding the market landscape. This includes:
- Assessing customer needs and pain points through surveys, focus groups, and interviews.
- Analyzing competitors to identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities.
- Monitoring industry trends to stay ahead of market shifts.
This data-driven approach helps PMMs tailor strategies that resonate with the target audience and differentiate their product from competitors.
2. Positioning and Messaging
A great PMM is adept at communicating a product’s differential advantage. They create positioning statements and messages that match the product’s value with the right customers. This typically requires working closely with the branding and content teams to make sure a steady story flows through every touchpoint.
3. Go-to-Market Strategy
Launching a product is one of the most pivotal tasks for a Product Marketing Manager. Their responsibilities include:
- Planning and executing a go-to-market (GTM) strategy.
- Coordinating with sales, product development, and customer success teams to ensure alignment.
- Establishing metrics to track the success of the launch, such as adoption rates, sign-ups, or revenue growth.
4. Sales Enablement
PMMs often act as the liaison between the product team and the sales team. They provide:
- Training material and sales collateral.
- Competitive battlecards.
- Product demos and presentations.
This ensures the sales team has everything they need to effectively communicate the product’s value during customer interactions.
5. Customer Feedback and Iteration
A PMM’s responsibilities don’t end after the product launch. Gathering customer feedback is crucial for product updates and future iterations. PMMs analyze what’s working (and what isn’t) to ensure sustained growth and adoption over time.
Measuring Success as a Product Marketing Manager
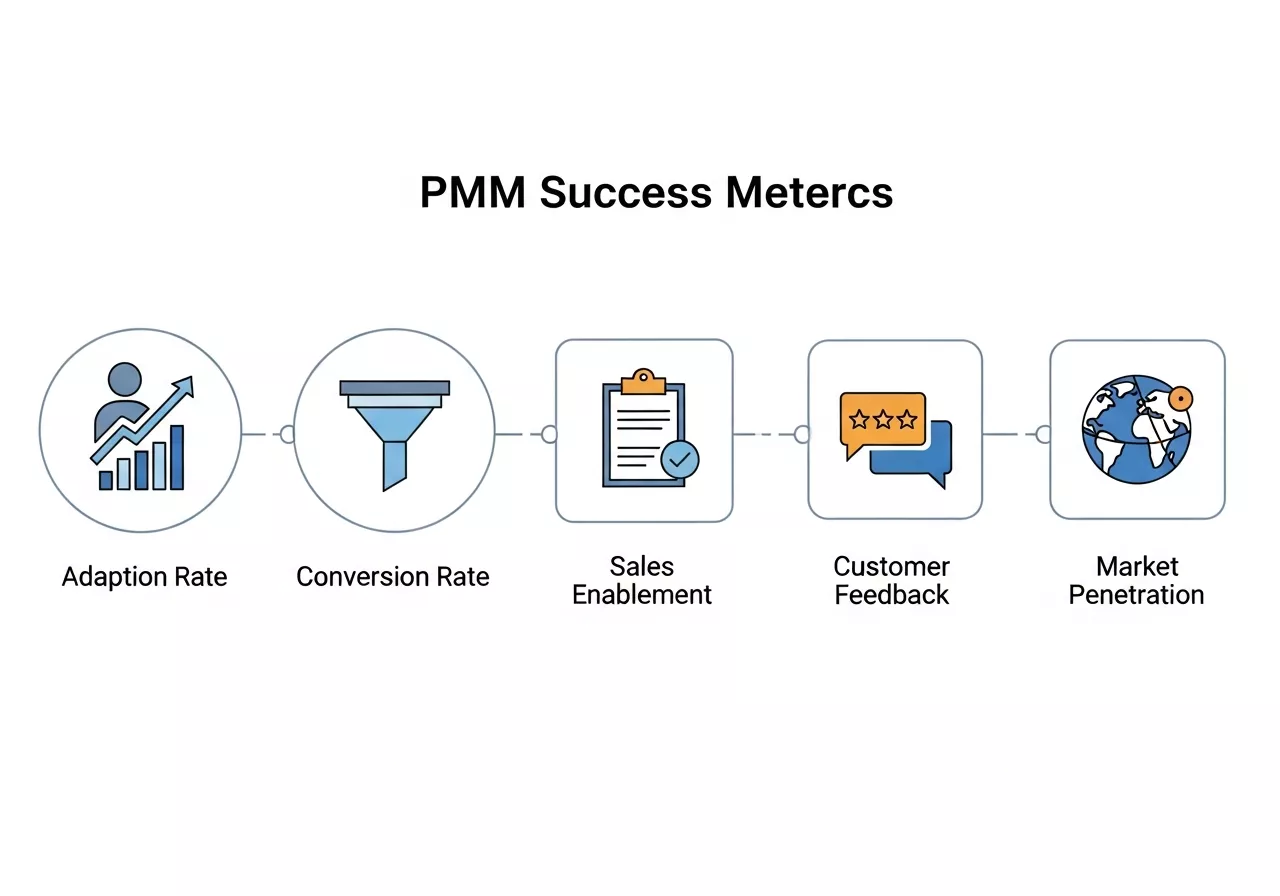
Measuring the effectiveness of a Product Marketing Manager (PMM) is crucial for understanding the impact of marketing strategies and ensuring product adoption. Success is not just about launching campaigns but driving measurable outcomes that align with business goals. PMMs use both quantitative and qualitative metrics to track performance, optimize strategies, and justify marketing investments.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for PMMs:
- Adoption Rate: Percentage of users actively using the product post-launch.
- Conversion Rate: Customers converting from free trials to paid plans.
- Sales Enablement Metrics: Number of deals influenced by marketing collateral.
- Customer Feedback Scores: Insights on product messaging and positioning effectiveness.
- Market Penetration: Growth in new markets or segments reached.
| Metric | Purpose | Ideal Frequency of Review |
|---|---|---|
| Adoption Rate | Evaluate product engagement | Monthly |
| Conversion Rate | Track marketing influence on revenue | Weekly/Monthly |
| Customer Feedback Scores | Improve messaging and product positioning | Quarterly |
| Sales Enablement Metrics | Support sales efficiency | Monthly |
| Market Penetration | Expand product reach | Quarterly |
Monitoring these KPIs allows PMMs to refine messaging, adapt GTM strategies, and collaborate effectively with product and sales teams.
Key Skills Required for a Product Marketing Manager
The role of a PMM is multi-faceted, which means they need a diverse set of skills to succeed. Here are some of the most important ones:
1. Strong Communication Skills
Whether it’s writing compelling messaging for a campaign, presenting to stakeholders, or training the sales team, clear and persuasive communication is critical.
2. Analytical Thinking
PMMs work with a wealth of data, from customer feedback to market trends. Being able to translate those insights into actionable strategies is key.
3. Market Knowledge
A deep understanding of the market, target customers, and competitive landscape is the foundation of effective product marketing.
4. Collaboration
Since PMMs interact with cross-functional teams, they need excellent collaboration skills to ensure diverse teams are working toward a unified goal.
5. Strategic Vision
Great PMMs see the big picture. They’re able to plan ahead, anticipate market trends, and position their products for long-term success.
6. Project Management
With multiple responsibilities and teams to manage during a product launch, PMMs need to stay organized, meet deadlines, and balance priorities effectively.
7. Adaptability and Creativity
No two markets are the same, and customer needs evolve. PMMs must adapt strategies to changing conditions while thinking creatively to solve challenges.
How to Become a Product Marketing Manager
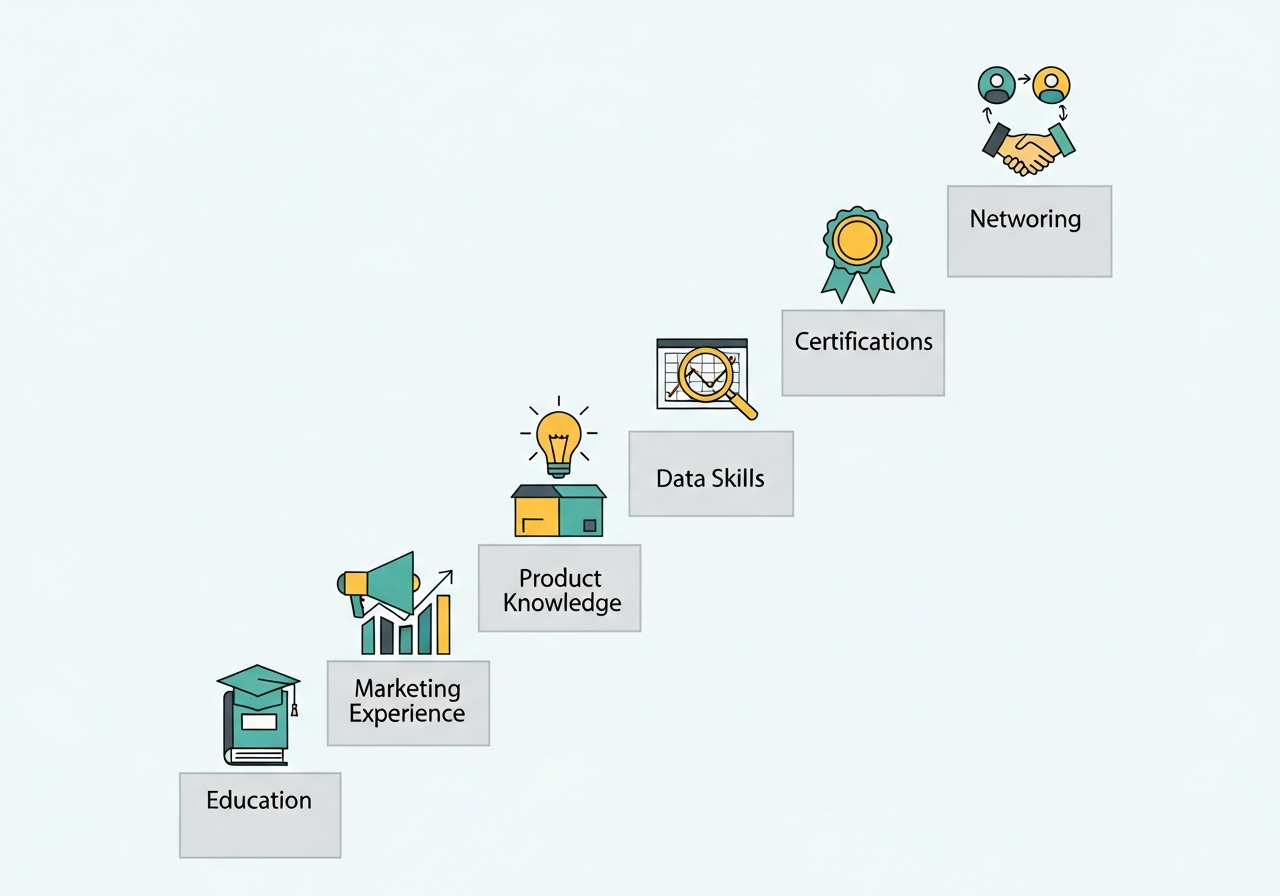
If you’re inspired to step into the world of product marketing, here’s a roadmap to help you get there:
1. Educational Background
While there’s no single path to becoming a PMM, most professionals in this field come from marketing, business administration, or related disciplines. A degree in marketing, communications, or business management is a solid starting point.
2. Gain Marketing Experience
Start by gaining hands-on experience in marketing. Whether it’s in content marketing, brand management, or digital marketing, build a strong foundation in understanding how to connect with consumers.
3. Learn Product Management Basics
Since PMMs often collaborate closely with product managers, understanding product development processes, including Agile or Scrum methodologies, is a huge advantage.
4. Develop Data Analysis Skills
Take courses in analytics tools or software like Google Analytics, Tableau, or Excel. Analytics is critical for understanding market trends, customer behavior, and measuring campaign performance.
5. Pursue Internships or Entry-Level Roles
Start with roles in marketing, sales enablement, or market research. These positions provide the hands-on experience you’ll need to understand customer needs, craft messaging strategies, and launch campaigns.
6. Get Certified
Certifications in relevant fields like digital marketing, social media, or product management can increase your hiring potential. Consider programs like HubSpot Academy, Pragmatic Institute’s Product Marketing Certification, or a Google Analytics certification.
7. Build a Portfolio
Highlight successful campaigns or analytical projects you’ve been part of. Showcasing concrete results, like increased adoption rates or revenue growth, will set you apart.
8. Network with Industry Professionals
Attend product marketing events, webinars, and meetups. LinkedIn is also a powerful tool to connect with PMMs, learn from their journeys, and stay updated on industry trends.
Tools and Technologies Every PMM Should Master
A Product Marketing Manager relies heavily on tools and technologies to analyze markets, engage customers, and support sales. Mastery of these platforms not only boosts efficiency but also strengthens decision-making capabilities.
Essential Tools for PMMs:
- Analytics Tools: Google Analytics, Mixpanel, Tableau – track user behavior, campaign performance, and customer trends.
- CRM Systems: Salesforce, HubSpot – manage leads, track customer journeys, and monitor sales pipeline.
- Marketing Automation: Marketo, Pardot – execute targeted campaigns and nurture prospects at scale.
- Competitive Intelligence Platforms: Crayon, SimilarWeb – monitor competitor positioning and industry movements.
- Collaboration Tools: Asana, Trello, Slack – streamline cross-team projects and align on timelines.
| Tool Type | Purpose | Example Platforms |
|---|---|---|
| Analytics | Measure user behavior & campaign performance | Google Analytics, Tableau |
| CRM | Track customers & leads | Salesforce, HubSpot |
| Marketing Automation | Automate campaigns & workflows | Marketo, Pardot |
| Competitive Intelligence | Monitor competitors & market trends | Crayon, SimilarWeb |
| Collaboration | Coordinate teams & projects | Slack, Asana |
By integrating these tools into daily workflows, PMMs can make data-driven decisions, improve GTM strategy, and deliver measurable business impact.
3. Emerging Trends in Product Marketing
The role of a Product Marketing Manager is constantly evolving, particularly in technology-driven industries where customer expectations and market dynamics change rapidly. Staying ahead of trends ensures PMMs can innovate while keeping the product relevant.
Key Trends Shaping Product Marketing:
- Personalization at Scale: AI-powered tools allow for tailored campaigns targeting individual buyer personas.
- Product-Led Growth (PLG): Shifting focus from traditional marketing to using the product itself as the main acquisition channel.
- Data-Driven Storytelling: Leveraging analytics to craft narratives that resonate with target audiences.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: PMMs working closely with UX, engineering, and sales teams to deliver cohesive customer experiences.
- Community Marketing: Building brand communities to encourage user-generated content, advocacy, and peer-to-peer recommendations.
| Trend | Implication for PMMs | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Personalization | Customize campaigns based on user data | Higher engagement & conversion |
| Product-Led Growth | Product as acquisition tool | Lower CAC & faster adoption |
| Data-Driven Storytelling | Decisions backed by analytics | More persuasive marketing |
| Cross-Functional Collaboration | Align product & marketing strategies | Improved launch effectiveness |
| Community Marketing | Leverage user advocacy & content | Stronger brand loyalty |
By embracing these trends, PMMs can future-proof their skills, influence product strategy, and deliver tangible business outcomes.
Why the Role of a Product Marketing Manager Matters
The Product Marketing Manager is a key player in a product’s success. They link the product itself to the reasons that a customer is going to solve those problems, and, in turn, drive adoption and revenue.
In today’s competitive landscape, the renaissance of PMMs is kicking in because in tech-driven industries, innovation must be conveyed to a range of audiences. The field is an exciting mix of creativity, strategy, and impact for those seeking a career.
So whether you’re a newbie in the work world or looking to pivot into a fast and high-stakes, high-rewarded role, product marketing could be your jam.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) – Product Marketing Manager
1. What does a Product Marketing Manager (PMM) do?
A PMM bridges the gap between product development, sales, and marketing. They research markets, define positioning, craft messaging, plan launches, enable sales teams, and ensure the product resonates with the target audience.
2. Do I need a specific degree to become a PMM?
No strict degree is required, but marketing, business administration, communications, or related fields are common. Practical experience and certifications often weigh more than formal education.
3. What skills are essential for a PMM?
Key skills include:
- Strong communication
- Analytical thinking
- Market knowledge
- Collaboration and cross-functional teamwork
- Strategic vision
- Project management
- Adaptability and creativity
4. How is PMM success measured?
Success is tracked through metrics such as:
- Product adoption and usage rates
- Revenue growth
- Sales team performance and enablement effectiveness
- Customer feedback and satisfaction
- Market share gains
5. Can a PMM work in any industry?
Yes. PMMs exist in tech, FMCG, SaaS, e-commerce, healthcare, and more. The principles of positioning, messaging, and go-to-market strategy apply across sectors.
6. What tools do PMMs commonly use?
Common tools include:
- Analytics: Google Analytics, Tableau, Excel
- CRM: Salesforce, HubSpot
- Marketing Automation: Marketo, Mailchimp
- Collaboration: Jira, Trello, Asana
- Content & Design: Canva, Figma
7. How do PMMs collaborate with other teams?
PMMs coordinate with:
- Product managers (feature priorities and development)
- Sales teams (enablement, demos, collateral)
- Marketing teams (campaigns, messaging, positioning)
- Customer success teams (feedback, adoption strategies)
8. What career growth opportunities exist for PMMs?
PMMs can progress to senior roles such as:
- Senior Product Marketing Manager
- Director of Product Marketing
- VP of Marketing
- Chief Marketing Officer (CMO)
learn more about: How to Build Your Product Marketing Strategy From Scratch