Product marketing is a strategic function that bridges product development, sales, and marketing. It focuses on understanding customer needs, crafting effective messaging, and driving product success. Key responsibilities include market research, positioning, and cross-functional collaboration to ensure growth and adoption.
Product marketing is probably one of the most misunderstood but critical functions in modern businesses. It lives at the intersection of product development, marketing, and sales, and ensures that a product not only launches properly, but continues to thrive once it does. But what is product marketing, and why does it matter so much?
In other words, if you are a marketing professional, product manager, or business owner, this post will geekify product marketing for you. We’re going to define product marketing, what it involves, it’s roles, it’s responsibilities and even touch on how it differs from the other marketing activities. When you’re done, you’ll understand better why product marketing is a fundamental growth engine for the business.
What is Product Marketing?
Product marketing, at its very essence, is about getting a product to market and making sure it succeeds once it gets there. This means getting to know the target audience inside out, offering a unique position for the product, and presenting its value in a customer irresistible way.
And while general marketing aims for brand awareness or lead generation for various products or services, product marketing zooms in on a singular product. This is to ensure that the product features, the messaging, the strategies all work harmoniously together to serve the needs of the intended users.
Key Definition
Product marketing is a strategic function that bridges the gap between product development and sales, focusing on understanding customer needs, crafting compelling positioning, and driving a product’s success in the market.
Understanding the Role of Product Marketing
What makes product marketing unique is its cross-functional nature. Product marketers often find themselves at the hub of various departments, seamlessly blending customer insights, product knowledge, and market demands into actionable strategies.
Core Elements of the Role
- Positioning and Messaging
Product marketers are responsible for telling the story of the product. They create value propositions and craft messages that resonate with the target audience.
- Go-to-Market Strategies
Every product launch requires a well-thought-out go-to-market plan. This includes setting launch goals, pinpointing target users, and coordinating with sales and marketing teams.
- Customer Insights
From surveys to focus groups, product marketers seek customer feedback to refine the product and messaging continually.
- Market Intelligence
Competitor analysis and industry trends are vital to ensure the product stands out and adapts to changing market dynamics.
Key Responsibilities of a Product Marketer
Now that we know what the role entails, what exactly does a product marketer do? Here are the primary responsibilities that define this role.
1. Market Research and Segmentation
Before positioning a product, product marketers invest significant time in understanding their audience. They segment the market and identify the best customer profiles to target.
2. Positioning and Differentiation
Imagine trying to sell noise-cancelling headphones in an already crowded market. Product marketers craft a unique positioning that highlights why their product is better or different from competitors.
3. Educating Internal Teams
Sales and support teams rely on product marketers to understand and explain the product’s key benefits and features. This often involves creating sales enablement materials like one-pagers or demo scripts.
4. Monitoring Performance
Once the product launches, product marketers track its performance across different metrics such as sales volumes, customer adoption rates, and levels of customer satisfaction.
5. Feedback Loop with Product Teams
Customer feedback collected by the product marketing team is fed back to the product development team to tweak existing features or plan new ones.
Building a Strong Product Marketing Strategy
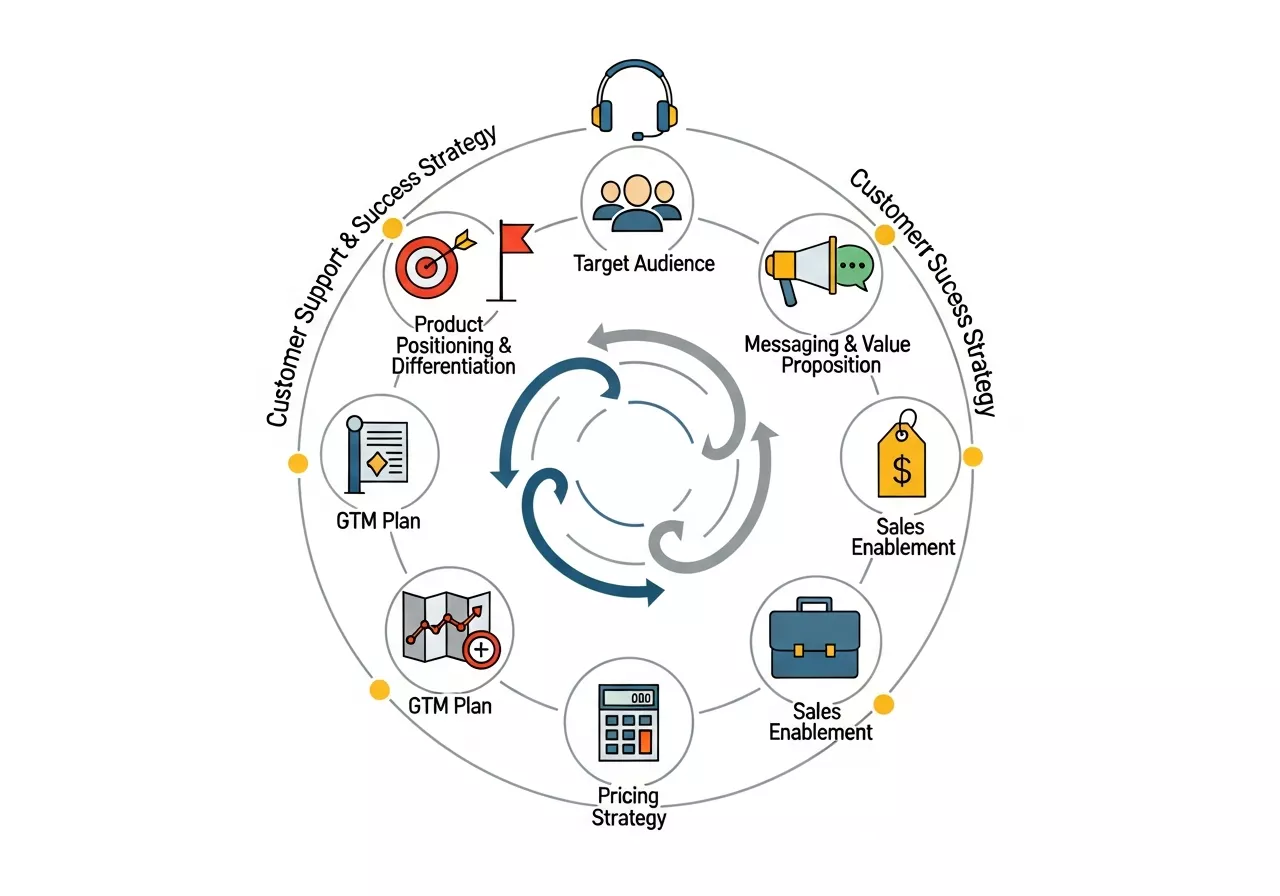
A well-defined product marketing strategy is essential for driving the success of any product. It’s the foundation that guides product marketers through every phase of product lifecycle—from ideation to post-launch. Developing a product marketing strategy requires a combination of data analysis, creativity, and a deep understanding of the market. The strategy sets the tone for how the product is positioned, who the target audience is, and how the product will be marketed.
Key Components of a Product Marketing Strategy:
-
Product Positioning & Differentiation: Clearly define how the product stands out in the marketplace compared to competitors. What makes your product unique? What pain points does it solve that no other product can?
-
Target Audience: Identify and segment your customer base. Knowing who the product is for helps in crafting tailored messaging and campaigns that speak directly to the needs of each segment.
-
Messaging & Value Proposition: Develop key messages that communicate the benefits of the product in a way that resonates with the target audience. This should include both the functional and emotional benefits.
-
Go-To-Market (GTM) Plan: Develop a comprehensive GTM plan that outlines product launch strategies, including the key channels for distribution, promotional tactics, and timelines.
-
Pricing Strategy: Understand how the product will be priced relative to competitors, and ensure that the pricing aligns with the perceived value in the market. Consider bundling, freemium models, or subscription-based pricing if applicable.
-
Sales Enablement: Provide your sales team with the necessary tools, materials, and training to sell the product effectively. This includes creating pitch decks, FAQs, objection handling materials, and detailed buyer personas.
-
Customer Support & Success Strategy: After the product launch, ensure a plan is in place to support customers and drive adoption. This includes training, creating knowledge bases, and offering ongoing customer service.
Table: Components of a Product Marketing Strategy
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Positioning | Define what sets your product apart and why it’s the best choice for your target audience. |
| Target Audience | Segment the market to identify and understand your ideal customer. |
| Messaging & Value Proposition | Craft compelling messages that highlight your product’s benefits and align with customer needs. |
| Go-To-Market (GTM) Plan | Develop a strategic plan outlining the product launch phases, key channels, and promotional tactics. |
| Pricing Strategy | Determine the most effective pricing structure for your product, considering market demand and value. |
| Sales Enablement | Provide resources, training, and materials to ensure your sales team is well-equipped to sell the product. |
| Customer Support & Success | Design customer support strategies to enhance user experience, increase retention, and drive satisfaction. |
Skills Required for Product Marketing Success
Product marketing stands apart because of its demand for diverse skills. These range from technical expertise to interpersonal abilities.
Must-Have Skills
- Market Research: Ability to understand your customers, competitors, and market landscape.
- Storytelling: Crafting compelling narratives that connect emotionally with customers.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Analyzing market data, customer insights, and performance metrics to guide strategies.
- Cross-Team Collaboration: Effectively working with teams across product, sales, and marketing.
- Communication Skills: Simplifying complex information while maximizing impact in both verbal and written formats.
Bonus Skills
- SEO knowledge to create customer-friendly content.
- Analytical tools like Google Analytics or Tableau to track product performance.
- Familiarity with user testing or A/B testing tools.
The Role of Data in Product Marketing: Measuring Success
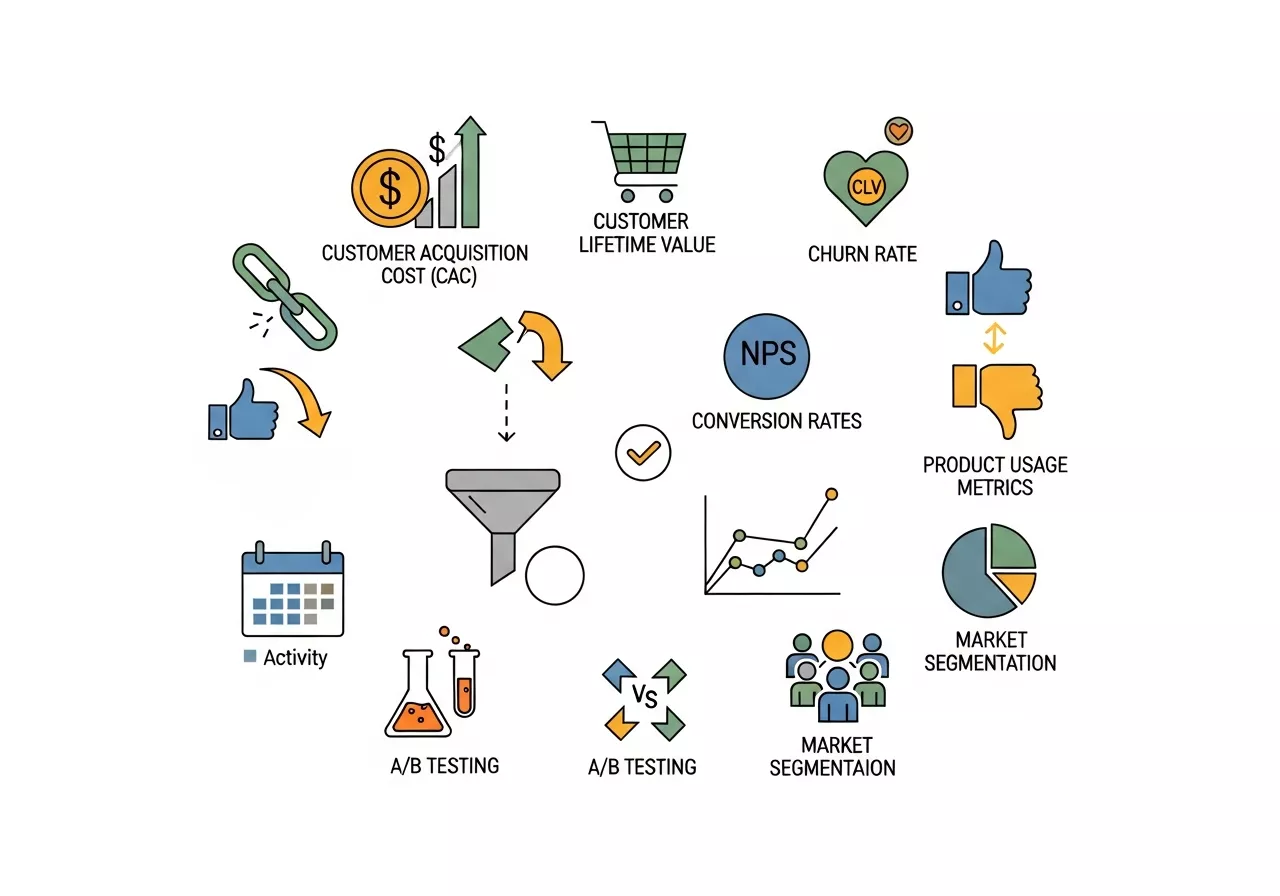
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, relying on intuition and experience alone is no longer sufficient. Product marketers must leverage data to measure the success of their strategies and optimize them in real-time. Data is not just a tool for measuring performance; it’s essential for making informed decisions and guiding future product marketing efforts.
Key Data-Driven Metrics for Product Marketers:
-
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): This metric helps determine the total cost of acquiring a new customer. It includes marketing expenses, sales efforts, and any other resources invested in attracting customers. Monitoring CAC helps ensure that the marketing spend is yielding the desired results.
-
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): CLV measures the total revenue a customer generates throughout their relationship with the company. The higher the CLV, the more successful your product marketing strategy is in building long-term relationships.
-
Churn Rate: The percentage of customers who stop using your product over a given period. Reducing churn is one of the key metrics that product marketers focus on post-launch.
-
Net Promoter Score (NPS): NPS is a key indicator of customer satisfaction and loyalty. Product marketers use it to gauge whether customers are likely to recommend the product to others.
-
Conversion Rates: This includes tracking how well your product is converting prospects into customers. It helps identify which parts of your sales funnel need optimization.
-
Product Usage Metrics: These are indicators such as daily active users (DAUs) or monthly active users (MAUs) that reflect how frequently customers are using the product. Higher engagement often correlates with product satisfaction and retention.
Using Data to Optimize Product Marketing:
-
A/B Testing: Test different messaging, landing pages, or pricing models to see which one resonates most with your target audience. This data-driven approach allows marketers to make improvements based on real customer behavior.
-
Customer Feedback Loops: Regularly collect and analyze feedback from customers through surveys, support interactions, and social media to adjust the product marketing strategy.
-
Market Segmentation Analysis: Segment your customers based on behaviors, preferences, and demographics. Tailoring your marketing efforts to specific segments helps increase relevance and boost conversion.
Table: Key Data-Driven Metrics for Product Marketing
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | Total cost spent on acquiring a new customer. Helps in assessing the efficiency of your marketing campaigns. |
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) | Predicts the total revenue a customer will generate during their relationship with the company. |
| Churn Rate | Measures the percentage of customers who discontinue using your product, a key metric for customer retention. |
| Net Promoter Score (NPS) | A measure of customer satisfaction and loyalty, based on the likelihood of customers recommending your product. |
| Conversion Rates | The percentage of visitors who take a desired action, such as purchasing the product or signing up for a demo. |
| Product Usage Metrics | Tracks engagement levels, including active users, retention, and usage patterns. |
Collaborating Across Teams: The Cross-Functional Nature of Product Marketing
Product marketing is unique because it requires constant collaboration with different departments within a company. As a product marketer, you’re often acting as the bridge between product development, sales, marketing, and customer support teams. Building strong interdepartmental relationships and facilitating smooth communication are vital to the success of the product.
Key Cross-Functional Collaborations:
-
Product Development Teams: Product marketers work closely with product managers and developers to ensure the product meets market needs and delivers on customer expectations. They provide valuable customer insights, feedback, and competitive analysis to guide product design and feature prioritization.
-
Sales Teams: Product marketers help sales teams by equipping them with the right tools and resources, such as sales playbooks, pitch decks, and training materials. They also provide critical input on target personas and customer objections, allowing sales reps to close deals more effectively.
-
Marketing Teams: While traditional marketers focus on brand awareness and engagement, product marketers focus on product-centric strategies. They work together to ensure that product launches are supported by cohesive campaigns and that product messaging aligns with the overall brand messaging.
-
Customer Support Teams: Product marketers provide training and resources for customer support teams so they can handle customer inquiries effectively. They also ensure that support teams are aware of any product updates or changes.
-
Customer Success Teams: Working with customer success ensures that the product delivers value long after the initial sale. Product marketers work to maintain customer satisfaction, retention, and engagement by providing insights into customer behavior and pain points.
Building Strong Cross-Functional Relationships:
-
Regular Communication: Hold regular meetings with different teams to ensure that everyone is aligned on goals, messaging, and product updates.
-
Feedback Loops: Encourage a continuous feedback loop between departments to ensure that everyone has the information they need to do their jobs effectively.
-
Shared KPIs: Work together with other departments to set shared performance metrics that align with overall business goals.
-
Cross-Departmental Training: Provide training sessions to help other teams understand the product’s value proposition, target audience, and messaging.
Table: Key Cross-Functional Collaborations in Product Marketing
| Department | Role in Product Marketing |
|---|---|
| Product Development | Collaborates with product marketers to ensure the product aligns with customer needs and market demands. |
| Sales | Provides sales teams with necessary tools, training, and insights to help them effectively sell the product. |
| Marketing | Partners with marketing teams to ensure product messaging aligns with broader brand initiatives. |
| Customer Support | Equips support teams with resources to handle customer inquiries and resolve issues efficiently. |
| Customer Success | Works with customer success to ensure product value is maintained post-launch, helping with retention and growth. |
Product Marketing vs. Other Marketing Roles
Many confuse product marketing with roles like brand marketing or content marketing. While there is some overlap, each function has a distinct focus.
Product Marketing vs. Brand Marketing
Brand marketing promotes the overall identity of a company (e.g., Nike’s “Just Do It”), while product marketing focuses on launching and scaling a product (e.g., Nike’s latest running shoes).
Product Marketing vs. Content Marketing
Content marketing creates valuable materials like blogs or eBooks, often to build audience relationships. However, product marketing uses content strategically to support product launches or nurture adoption.
Product Marketing vs. Growth Marketing
Growth marketing aims to acquire leads and scale conversions. Product marketing complements this by ensuring that those leads understand and value the product they are adopting.
Trends and Future of Product Marketing

The world of product marketing is evolving as businesses and customer expectations shift. Here’s what lies ahead.
AI-Driven Insights
AI tools can help product marketers analyze patterns in customer behavior, making segmentation and personalization more accessible.
Increased Focus on Customer Retention
Acquiring a customer is expensive. Modern product marketers focus on driving long-term engagement and repeat purchases.
Rise of Product-Led Growth
More companies are adopting a product-led growth model, focusing on delivering value through the product itself and letting the product drive user adoption.
Integrated Platforms
With platforms like HubSpot and Salesforce, marketing automation allows marketers to manage everything from lead generation to customer feedback seamlessly.
Why Product Marketing is Crucial to Business Success
Even with the most innovative products, without product marketing, they may not resonate with the target market. This is a strategic capability that makes sure your product is in the right hands and makes an impact with the right people.
Whether you’re introducing a new product or fine-tuning your existing product, product marketing can make or break your success.
If you want to take your product marketing to the next level, investing in the tools and resources you need to hone your strategy is an excellent place to start. Make sure to train your team first on skills to position unmanaged products effectively and create a dynamic, responsive timeline to the market changes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Product Marketing
1. What exactly does a product marketer do?
A product marketer is responsible for ensuring that a product is successfully launched, marketed, and positioned in the market. Their role spans from understanding customer needs, crafting compelling messaging, and coordinating with cross-functional teams, to tracking product performance and refining strategies based on feedback and data. They are the bridge between product development, sales, and marketing.
2. How is product marketing different from other types of marketing?
While general marketing focuses on promoting a brand or a range of products, product marketing is specifically centered around one product. It involves creating and executing strategies that position the product effectively, define its unique selling points, and ensure it meets the needs of the target market. It also works closely with sales teams to drive conversions and works with product teams to provide customer feedback that helps refine the product.
3. What are the key skills required for product marketing?
Successful product marketers need a mix of technical, strategic, and interpersonal skills. Key skills include:
- Market Research to understand customer needs and competitor landscapes.
- Storytelling to create compelling product narratives.
- Data-Driven Decision Making for optimizing strategies based on analytics.
- Cross-Department Collaboration to work seamlessly with sales, product, and customer support teams.
- Communication Skills to clearly articulate product value and collaborate across teams.
4. What is a go-to-market (GTM) strategy and why is it important?
A go-to-market (GTM) strategy is a plan that outlines how to launch a product, reach the target audience, and achieve sales goals. It includes product positioning, messaging, promotional strategies, pricing, and distribution channels. A solid GTM strategy ensures that the product reaches the right people at the right time with the right message, helping to maximize its chances for success.
5. How does product marketing use data to improve strategy?
Data plays a central role in refining product marketing strategies. Product marketers use metrics such as Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), churn rate, and conversion rates to assess the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and product performance. They also analyze customer feedback, usage patterns, and A/B testing results to make data-driven decisions and continuously optimize messaging and positioning.
6. What is the difference between product marketing and brand marketing?
Brand marketing is focused on building and promoting the overall identity of a company or brand (e.g., Nike’s “Just Do It”). Product marketing, on the other hand, is focused on promoting specific products, such as a new pair of Nike running shoes. While brand marketing aims to establish long-term brand recognition, product marketing drives short-term sales and product adoption.
7. Can product marketing be successful without cross-functional collaboration?
No. Product marketing thrives on collaboration. Product marketers work closely with teams from sales, product development, customer support, and other marketing functions to ensure that everyone is aligned with the product’s goals, messaging, and positioning. Strong cross-functional collaboration is essential for a successful product launch and sustained product growth.
8. How can I ensure my product marketing strategy is successful?
To ensure a successful product marketing strategy:
- Understand your audience by conducting thorough market research and segmentation.
- Develop clear messaging that communicates the unique value of your product.
- Implement a solid go-to-market strategy with clear launch goals and timelines.
- Use data to track performance and continuously adjust tactics based on feedback and market insights.
- Foster collaboration between all teams (product, sales, marketing, support) to ensure everyone is working toward the same goal.
9. What are some common mistakes in product marketing?
Some common mistakes in product marketing include:
- Lack of market research, leading to misaligned product positioning.
- Overcomplicating messaging, making it difficult for customers to understand the product’s value.
- Ignoring customer feedback, which can lead to missed opportunities for improvement.
- Poor collaboration with sales teams, which can result in missed revenue opportunities and inconsistent messaging.
10. How can AI help in product marketing?
AI tools can significantly enhance product marketing by providing deeper customer insights, automating repetitive tasks, and helping with segmentation and personalization. AI can analyze large sets of data to uncover trends in customer behavior, predict future trends, and even personalize marketing messages in real time. AI-driven insights also allow product marketers to refine their strategies based on real-time feedback and market dynamics.
Learn more about: What Is Digital Product Marketing and Why It Matters