In today’s highly competitive market, relying on intuition alone is no longer effective. Companies that succeed consistently are those that make smart decisions based on accurate data.
Using data-driven insights in product marketing is not just a trend—it’s the backbone of modern strategy. When done correctly, it helps businesses understand their customers better, craft messages that resonate, and make marketing investments that actually pay off.
Let’s explore how businesses can apply this approach in real-world scenarios to get better outcomes from their product marketing efforts.
Why Data-Driven Insights Matter in Marketing

Marketing has changed. It’s no longer about just pushing a product and hoping for the best. Now, it’s about understanding the behavior, preferences, and habits of your target audience.
When businesses use data correctly, they can:
- Avoid wasting money on tactics that don’t work.
- See what their audience really wants.
- Respond to market trends faster than competitors.
This insight is especially valuable in product marketing, where small changes in messaging or pricing can make a huge difference. While focused on marketing, data-driven insights can also be applied in consumer education, such as understanding the 5 P foods to avoid and why.
How to Collect the Right Data
Before making any decisions, you need the right kind of data. But it’s not just about collecting information—it’s about knowing what matters.
Start with these sources:
Customer Feedback
Talk to your users. What do they like? What frustrates them? Real feedback often reveals more than numbers.
Website Behavior
Use analytics tools to track how visitors move through your site. What do they click? Where do they drop off?
Sales Data
Which products are selling? When are they selling? Sales trends offer clues about what your audience values.
Market Research
Competitor analysis, surveys, and industry reports help you see the bigger picture.
The key is to combine these data points. One source alone may not be enough, but together, they give you a complete view.
Turning Data Into Insights
Data doesn’t mean anything unless you know how to read it. You don’t need to be a data scientist, but you should know how to ask the right questions.
Look at:
- Patterns in customer behavior.
- Peaks and drops in product interest.
- Time spent on specific product pages.
- Which marketing campaigns led to the most conversions?
For example, if you see that most users abandon a product page within 10 seconds, it may be a signal that your content isn’t engaging—or that your pricing is off.
By spotting these trends early, you can adjust before losing potential customers.
The Role of Product Life Cycle in Product Marketing
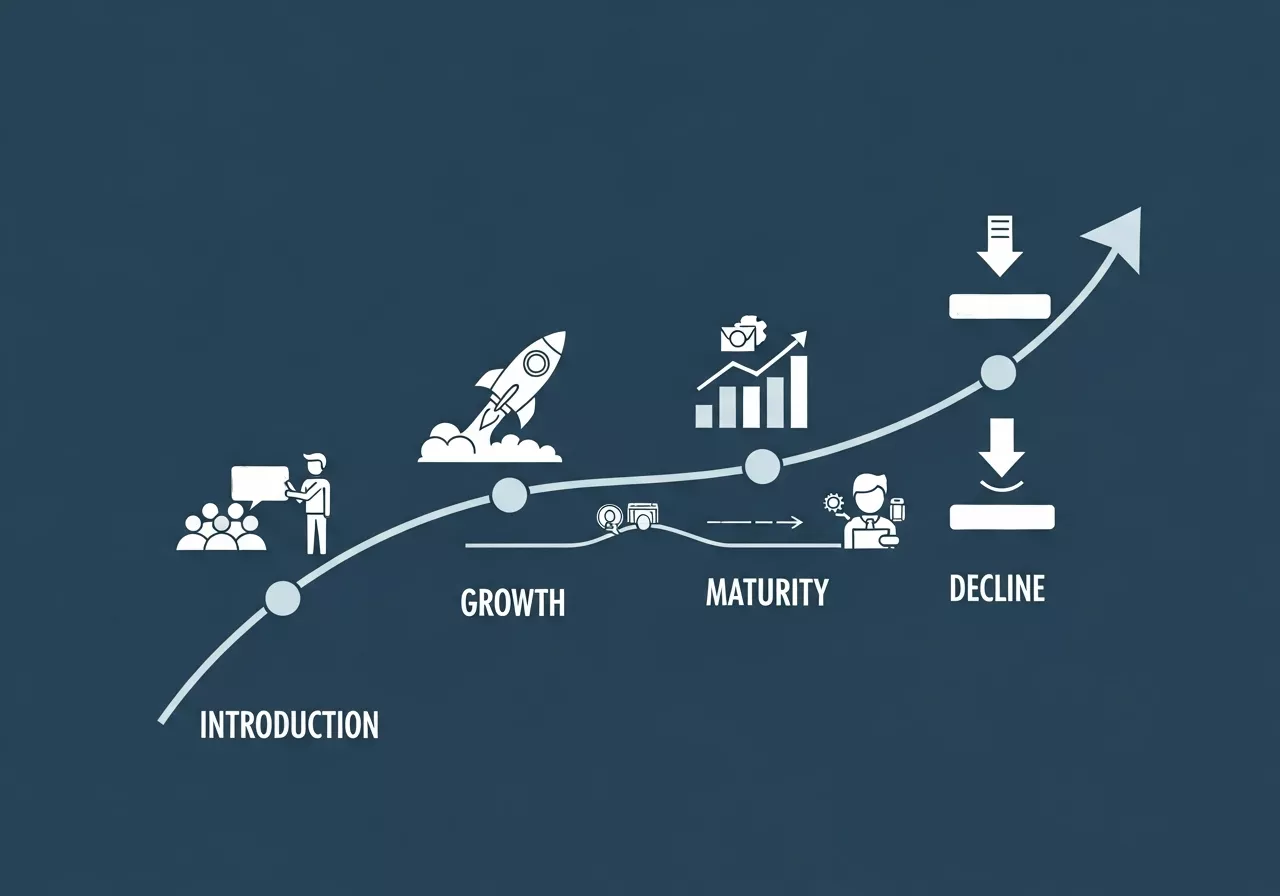
The Product Life Cycle in Marketing (PLC) is a critical concept that marketers must understand to craft strategies that suit each stage of their product’s journey—from introduction to decline. Every product goes through several stages, and knowing where your product is within the cycle helps tailor your marketing strategies effectively.
Understanding the Stages of the Product Life Cycle
- Introduction: In this phase, a product is launched into the market. Marketing efforts focus heavily on building awareness and educating the target audience. During this stage, data-driven insights help to identify the most effective channels to reach early adopters and make the initial push for sales.
- Growth: This stage is marked by rapid sales growth and increased market acceptance. Here, businesses need to analyze customer data to understand which features are most appreciated by customers, fine-tuning messaging accordingly to maximize engagement.
- Maturity: When the product reaches its peak in sales, marketers must defend market share and optimize profitability. By tracking sales data, they can identify the product’s strengths and weaknesses and determine areas for innovation.
- Decline: As sales start to decline, companies may choose to withdraw the product or reposition it. Data insights can inform decisions like reducing the product’s price, targeting a different audience, or enhancing the product with new features.
Why the Product Life Cycle Matters in Product Marketing
Understanding where your product is in the Product Life Cycle allows you to:
- Align marketing efforts with the product’s current stage.
- Adjust pricing strategies to boost sales in the maturity phase.
- Anticipate and prepare for product decline with data-driven exit strategies.
The Product Life Cycle is a valuable tool for guiding decisions on promotions, distribution channels, and customer retention. By leveraging data insights during each phase, businesses can maximize product profitability and extend the life of their offerings.
| Stage | Key Marketing Focus | Data-Driven Insight Use |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction | Awareness and adoption | Track customer acquisition, initial product feedback |
| Growth | Customer retention and loyalty | Analyze user behavior and adjust messaging accordingly |
| Maturity | Defend market share, optimize profitability | Review sales trends and product feature popularity |
| Decline | Reposition or phase out | Identify areas for improvement or pivot to new markets |
The Power of Storytelling in Product Packaging Design
In today’s competitive market, the visual and emotional appeal of a product often makes the difference between a sale and a pass. Storytelling in Product Packaging Design is one of the most effective ways to communicate your product’s value and connect with customers on a deeper level.
Why Storytelling Matters in Product Packaging
Product packaging is no longer just about functionality; it’s a critical touchpoint in the customer journey. A well-designed package tells a story that resonates with the target audience, making the product stand out on the shelf and reinforcing brand values. Storytelling is especially important in the context of product marketing because it:
- Engages Consumers Emotionally: A compelling narrative can create an emotional connection, leading to stronger brand loyalty.
- Differentiates Your Product: In crowded marketplaces, storytelling makes your product memorable. Consumers are more likely to purchase a product if its packaging stands out and tells a story they can relate to.
- Conveys Brand Identity: Packaging is an extension of your brand. The visuals, colors, and language used can express the brand’s personality, values, and mission.
Using Data to Shape Storytelling in Packaging Design
Just as in any other part of product marketing, data-driven insights can guide packaging decisions. For example:
- If customer feedback reveals a growing demand for eco-friendly products, your packaging design can emphasize sustainability.
- Website behavior data might show that customers engage more with content that highlights the natural ingredients in a beauty product, suggesting that packaging should feature such elements prominently.
The Intersection of Data and Creativity in Packaging
While creativity is essential for good packaging, data ensures that the story resonates with the right audience. By combining storytelling with insights from customer feedback and behavior analytics, companies can craft packages that don’t just look good—they sell products.
Leveraging Customer Feedback for Effective Product Marketing

No marketing strategy is complete without understanding your customers’ opinions and experiences. Customer Feedback is a goldmine for refining your product marketing strategies and ensuring that your offerings meet the needs of your target audience.
The Value of Customer Feedback in Product Marketing
Customer feedback provides direct insight into what your audience likes, dislikes, and expects from your product. Collecting and analyzing this data is crucial for:
- Refining Product Features: Customers may request certain features that, if implemented, could significantly improve satisfaction and sales. By listening to feedback, companies can make necessary improvements before a product reaches the market’s saturation point.
- Optimizing Marketing Campaigns: If certain messaging resonates more with users, marketing campaigns can be adjusted to better match consumer preferences. This data can be gathered from customer surveys, social media interactions, and review platforms.
- Improving Customer Retention: By responding to feedback and showing customers that their opinions are valued, companies can enhance loyalty and reduce churn. Retaining existing customers often costs less than acquiring new ones, making it essential for long-term success.
Types of Customer Feedback to Collect
- Surveys: Ask direct questions about their experience with your product. These can be sent via email, social media, or integrated on your website.
- Product Reviews: Analyze reviews on e-commerce sites to gauge customer satisfaction and uncover areas for improvement.
- Social Media Sentiment: Monitor social media platforms for mentions of your product. Positive or negative comments can provide real-time insights.
- Customer Support Interactions: Track common queries or issues customers report through your support channels.
Turning Feedback Into Actionable Insights
Collecting feedback is one thing; turning it into product marketing strategies is another. Here’s how businesses can translate feedback into action:
- Product Refinement: If customers highlight issues with usability, consider revising the design or user interface.
- Messaging Adjustment: If a product’s benefit is not clear to users, tweak marketing materials to highlight it more prominently.
- Customer Service Improvements: Negative feedback on service can signal the need for improved training or processes.
Applying Insights to Product Strategy
Now comes the most important part: using the insights to take action.
Refining the Message
Maybe your audience responds more to benefit-driven language than feature lists. If your data shows higher conversion rates with simpler headlines, adjust all future campaigns to follow that format.
Optimizing Pricing
If customers are clicking through but not buying, the issue could be price. Test different pricing strategies, and use A/B testing to see what works.
Product Improvements
Feedback might point out that customers want a specific feature. If enough people ask for it, adding that feature could give your product an edge in the market.
Data-driven product marketing is not just about selling what you have. It’s about shaping what you offer to match what people need.
Using the Right Tools
You don’t need expensive platforms to start. There are many affordable or free tools that can help you track and analyze data:
- Google Analytics – Great for understanding user behavior.
- Hotjar – Shows heatmaps and user interaction.
- HubSpot – Combines CRM with marketing insights.
- Tableau or Looker Studio – For visualizing complex data in an easy-to-understand format.
Choose tools based on your goals and your team’s skill level. Start small and scale as you grow.
Data Ethics and Trust
When collecting data, always be transparent. Users want to know how their data is used, and violating trust can damage your brand.
Be sure to:
- Follow privacy laws like GDPR or CCPA.
- Keep customer data secure.
- Allow users to opt out of tracking when possible.
Being honest about data usage not only keeps you legally safe but also builds a stronger relationship with your audience.
Real-World Example: Data-Driven Success

A mid-sized skincare brand once relied on influencer partnerships to drive sales. However, growth had stalled. After reviewing customer data, they noticed that:
- Users under 25 were not buying, despite being the target.
- Blog posts on natural ingredients had more engagement.
- Product pages with reviews saw higher conversions.
They shifted focus. Instead of chasing influencers, they invested in content that explained product ingredients and displayed more customer reviews.
Within three months, their conversion rate increased by 27%. This shift was purely based on listening to the data.
Challenges in a Data-Driven Approach
No strategy is without roadblocks. With data, some common problems include:
- Overload of information: Too much data can lead to confusion.
- Misinterpretation: Numbers don’t always mean what you think they do.
- Delayed action: Some teams collect data but fail to act on it.
The way around this is simple: focus only on the metrics that tie directly to your goals. Always ask: “What will I do with this data?”
Conclusion
In today’s competitive environment, leveraging data-driven insights and incorporating customer feedback into every aspect of your product marketing strategy is essential for success. Marketers must continuously evolve, responding to shifts in the product life cycle, designing compelling narratives through storytelling in packaging, and always listening to their audience.
The future of product marketing isn’t just about creating great products—it’s about creating products that truly align with customer desires and needs. By embracing these strategies, businesses can ensure their marketing efforts remain relevant and impactful, even as market dynamics continue to change.
FAQs
1. What is product marketing?
Product marketing is the process of bringing a product to market and promoting it in a way that resonates with the target audience. It involves understanding customer needs, positioning the product effectively, crafting compelling messaging, and using data-driven insights to maximize sales and engagement. Product marketing focuses not just on selling a product but ensuring it meets market demand.
2. Why are data-driven insights important in product marketing?
Data-driven insights help businesses make informed decisions rather than relying solely on intuition. By analyzing customer behavior, sales trends, and market research, marketers can optimize campaigns, refine messaging, and even improve products. Using insights allows companies to respond faster to market changes, reduce wasted marketing spend, and increase conversion rates.
3. How does the Product Life Cycle in Marketing affect product strategies?
The Product Life Cycle in Marketing (PLC) outlines the stages a product goes through: Introduction, Growth, Maturity, and Decline. Understanding a product’s stage helps marketers:
- Tailor campaigns to attract the right audience
- Adjust pricing strategies
- Plan product improvements or extensions
- Predict when to reposition or phase out products
By aligning marketing strategies with the PLC, businesses can make smarter decisions and extend product profitability.
4. How can storytelling in product packaging design improve sales?
Storytelling in Product Packaging Design uses the product’s packaging to communicate a narrative that resonates with customers. Effective storytelling can:
- Build emotional connections with consumers
- Differentiate products in a crowded market
- Reinforce brand identity
- Influence purchase decisions
Combining storytelling with data-driven insights ensures that the packaging appeals directly to your target audience.
5. What role does customer feedback play in product marketing?
Customer feedback is essential for understanding what works and what doesn’t. It allows marketers to:
- Improve product features based on real user suggestions
- Optimize marketing messages to reflect customer preferences
- Identify pain points that affect customer satisfaction
- Enhance loyalty by responding to concerns and showing that customer voices matter
Using feedback alongside analytics ensures marketing decisions are grounded in real user experiences.
6. What are some tools for collecting and analyzing marketing data?
Several tools help marketers track, analyze, and visualize data effectively:
- Google Analytics – Tracks website behavior and user engagement
- Hotjar – Provides heatmaps and insights into user interactions
- HubSpot – Integrates CRM with marketing data
- Tableau / Looker Studio – Visualizes complex datasets for easier interpretation
Choosing the right tools depends on your team’s skills, goals, and the complexity of your data needs.
7. How can small businesses apply data-driven product marketing?
Small businesses can start small by focusing on key metrics like website behavior, sales trends, and customer feedback. They don’t need expensive tools—free or affordable platforms like Google Analytics, Hotjar, and social media analytics can provide actionable insights. The key is to act on the data, not just collect it.
8. How do I ensure ethical use of customer data in marketing?
Ethical data use is crucial to maintaining trust. Companies should:
- Follow privacy regulations such as GDPR or CCPA
- Keep customer data secure
- Be transparent about data collection and usage
- Allow customers to opt out of tracking
Being ethical with data not only avoids legal issues but also strengthens brand credibility.
9. Can product marketing strategies help during product decline?
Yes. Even in the decline phase of the Product Life Cycle, product marketing can help by:
- Repositioning the product for a new audience
- Offering discounts or bundling with other products
- Using customer feedback to introduce improvements or complementary products
Strategic marketing at this stage can extend the product’s lifecycle or maximize remaining revenue.
10. What is the future of product marketing?
The future of product marketing is data-driven, customer-focused, and creative. Companies that combine insights from analytics and feedback with storytelling and compelling product experiences will remain competitive. Product marketing will continue to evolve, emphasizing personalized experiences, sustainability, and meaningful connections with customers.
Learn more about: The Psychology Behind Successful Product Marketing





